Soft physics
This guide will explain the concept behind soft physics and how to create the different kind of soft physics entities.
Basic concept
To create soft bodies of any kind there are currently two main components that are used to link multiple entities together:
SoftLinkComponentwill link the containing entity with another. The target is specified by id within the component. The component is used by other components to create an outline for soft bodies.SoftStructureComponentwill basically do the same but with multiple targets. The component is used to create structural integrity when creating a soft body from multiple entities.
Both components specify the link length between the entities.
It is not required to specify the link length on entity creation, because they are automatically set when the entities
are processed by the SoftPhysicsSystem.
If one or more of the link node entities move before the link lengths are initialized, this might lead to unwanted
behavior.
Therefore it is recommended to explizitly set the link lengths.
The SoftPhysicsSupport class (see below) can automate the link length initialization.
Soft physics entities
Ropes
A rope is simply a chain of entities linking each other using the SoftLinkComponent.
To create a rope you can create a chain of entities each linking to the next one using the SoftLinkComponent.
To render the rope add a RopeComponent and a RopeRenderComponent to the first entity within the chain.
The RopeComponent will build a comfortable list of entities contained within the rope.
The RopeRenderComponent will actually render a smoothed line between the entities from the node list within the
RopeComponent.
The SoftPhysicsSupport helps with the rope creation.
The createRope method will create a linked list of prepared rope entities that you can customize further.
The return value is a specified list that simplyfies access to some 'special' entities within the rope.
The root entity will be the one containing the RopeComponent.
The end entity will not have a SoftLinkComponent.
// creates 8 linked entities
var rope = SoftPhysicsSupport.createRope($(4, 10), $(4, 50), 8, engine.environment());
// add rendering (.root() entity will contain the RopeComponent)
rope.root().add(new RopeRenderComponent(Color.MAGENTA, 2));
// customize the links flexibility
rope.forEach(node -> node.tryGet(SoftLinkComponent.class).ifPresent(link -> link.flexibility = 50));
// customize friction
rope.forEach(node -> node.get(PhysicsComponent.class).friction = 1);
// remove physics from the end node to make it fix
rope.end().remove(PhysicsComponent.class);
Soft Bodies
Soft bodies are (rounded) closed polygons that can collide with each other which will create a 'jelly' effect.
Creating soft bodies is similar to creating ropes.
Start by creating a loop of entities each linking to the next one using the SoftLinkComponent.
In contrast to building a rope the last element of the chain must link back to the first element.
The SoftBodyComponent will build a comfortable list of entities contained within the outline of the body.
This component is also required to use other functionality e.g. rendering and shape matching.
The entity containing the SoftBodyComponent will be referred as the soft body entity.
The SoftBodyRenderComponent will actually render a polygon created by the the entities from the node list within the
SoftBodyComponent.
It is a lot easier to create soft bodies using the SoftPhysicsSupport class.
The support class can create soft bodies with and without structural integrity.
The result of the helper method will also be a specialized list that allows direct access to the root entity etc..
// creates a soft body with three nodes
var polygon = Polygon.ofNodes($(20, 2), $(40, 3), $(30, 20))
var softBody = SoftPhysicsSupport.createStabilizedSoftBody(polygon, environment);
// enables rendering
softBody.root().add(new SoftBodyRenderComponent(Color.ORANGE);
// adds all soft body entities to the environment
engine.environment().addEntities(softBody);
Preserving shape
To preserve the shape of the soft body you have created, add a SoftStructureComponent to some of the nodes and link
them to other ones.
This will add some basic structural integrity and works pretty well for some shapes.
If the soft body gets more complex the shape may quickly collapse in certain situations.
To preserve the original shape, simply add a SoftBodyShapeComponent to the soft body entity.
This component will add shape matching to the soft body which will instantly stabilize the original shape.
The component can be configured to disable rotation of the shape, if the goal is to keep the shape upright.
The component can also be configured to disable movement to fix the shape position as well.
Adding a SoftBodyShapeComponent to an entity might lead to unwanted motion when entity shape is deformed by collision.
This sadly cannot be avoided.
But to mitigate the issue, try experimenting with entity friction and dead zone value of the shape component.
This image visualizes the outline links, the soft structure links and the links between the soft body and the shape matching one.
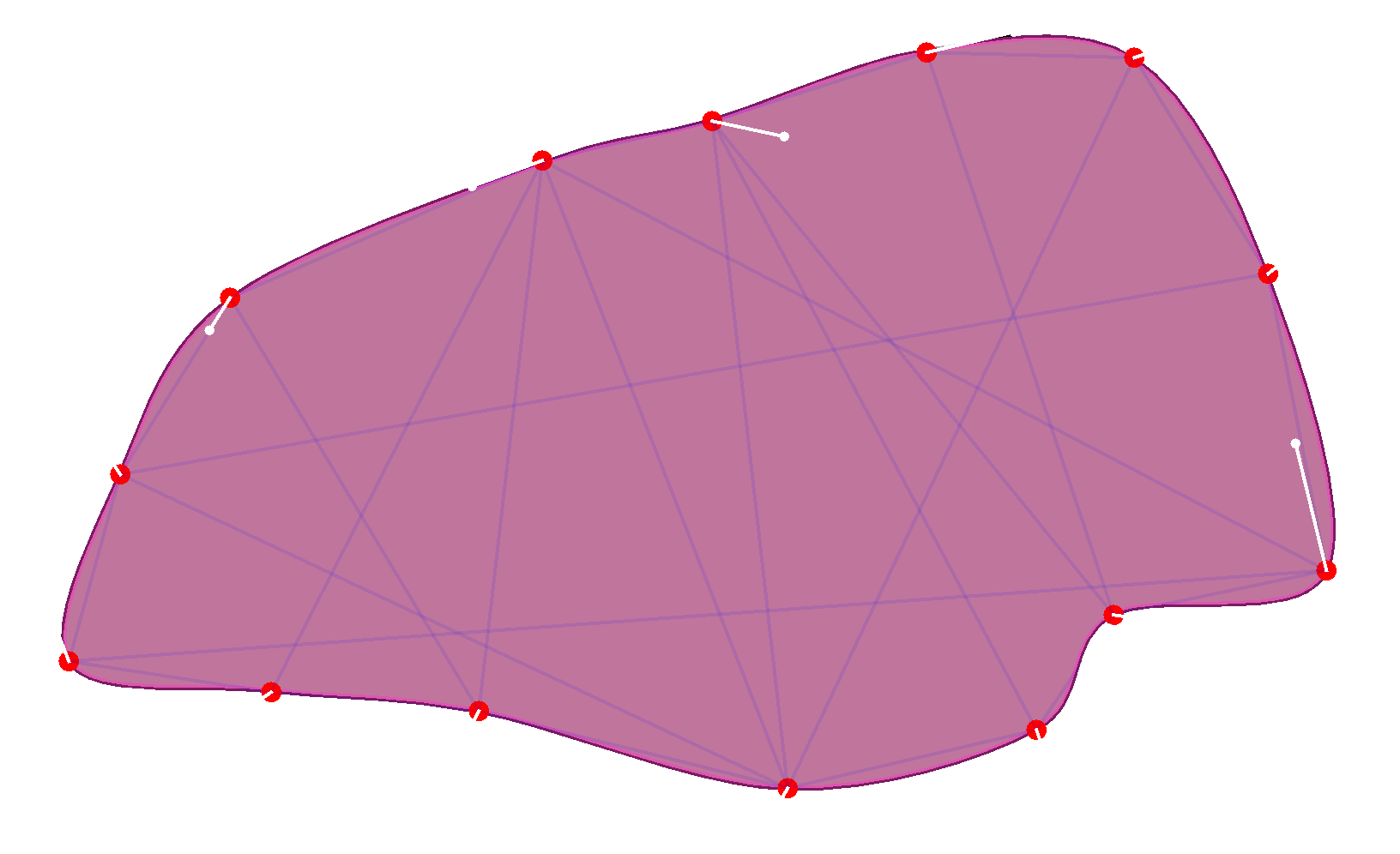
Soft body collisions
To add collisions between soft bodies add the SoftBodyCollisionComponent to all soft bodies that should collide
with each other.
Soft body collisions are far from perfect.
ScrewBox uses a mix of point in polygon and bisector ray collision preventions.
Collisions may add lots of momentum to the soft body.
Experiment with the different configuration properties of the SoftStructureComponent, SoftLinkComponent and the
SoftBodyShapeComponent to get the best results.
Expand size
To expand a soft body add ad SoftbodyPressureComponent and specify the pressure value, that you want to apply.
Avoid applying very low negative values because this will mess up the body when the structural integrity is lower
than the pressure.
Cloth
Cloth entities are a special kind of soft body.
Cloth entities have an outline linked by SoftLinkComponents.
But they also have a mesh of additional entities within that are linked using SoftStructureComponent.
These internal links will provide a kind of cloth like integrity.
The root node will contain a SoftBodyComponent but also a ClothComponent that provides direct access to the mesh of
linked entities.

The ClothRenderComponent allows rendering of the cloth using a mesh shading algorithm to create a 3D like effect.
The rendering can be customized with textures, detail level and color.
Creating cloth is no fun.
To make it easier use the SoftPhysicsSupport class.
// creates the cloth entities using a 16 by 16 mesh
var cloth = SoftPhysicsSupport.createCloth(Bounds.$$(0,0,128,256), Size.of(16, 16), e.environment());
// add rendering of a flag with white background
cloth.root().add(new ClothRenderComponent(), x -> {
x.texture = Sprite.fromFile("flag.png");
x.backgroundColor = Color.WHITE;
});
// attach the top border of the flag to the game world
cloth.topBorder().forEach(entity -> entity.remove(PhysicsComponent.class));